What is the Difference Between Gpu Scaling and Display Scaling
GPU scaling and display scaling differ in their function and purpose. GPU scaling adjusts the resolution of older games to fit modern displays, while display scaling maintains the size and readability of on-screen elements at high resolutions.
If you’re a gamer, GPU scaling is ideal for maintaining the seamless gaming experience on modern displays, whereas display scaling is beneficial for displaying crisp and clear visuals on high-resolution screens. However, GPU scaling may add some input latency, which could be noticeable in gaming.
We’ll delve deeper into GPU scaling and display scaling, explaining their differences, functions, and benefits. Whether you are a gamer or use high-resolution screens, understanding GPU scaling and display scaling is essential for enhancing your visual experience.
Gpu Scaling Vs. Display Scaling
GPU scaling and display scaling have different purposes. GPU scaling is best for gamers who want to maintain a seamless experience with older games while display scaling is best for achieving clarity and readability on high-resolution screens, especially for UI elements.
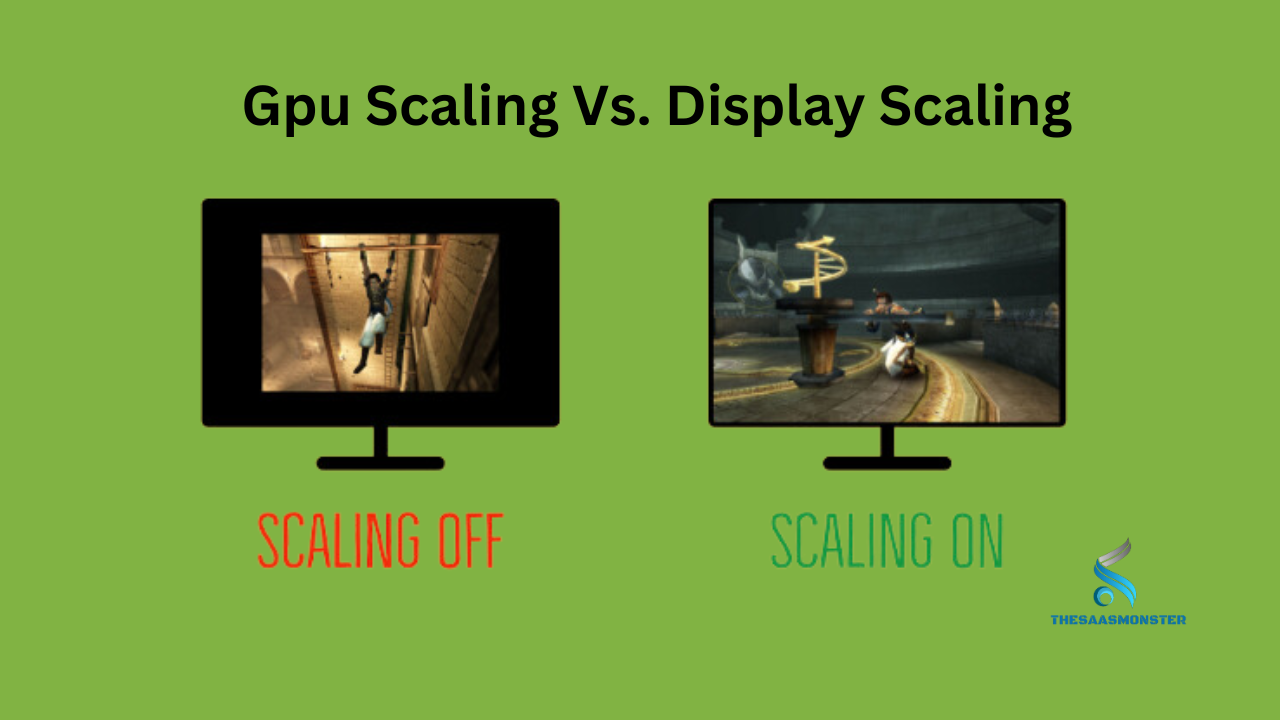
GPU Scaling vs. Display Scaling When it comes to gaming, scaling is an essential part of the process. It refers to the way an image is stretched or compressed to fit a particular display resolution. But not all scaling techniques are created equal. Two types of scaling in gaming are GPU scaling and display scaling. What is GPU Scaling? GPU scaling, also known as hardware scaling, is when the GPU or graphics card scales up a lower resolution image to fit a higher resolution screen.
This technique bypasses the display’s scaler and uses the graphic card’s scaler to avoid interferences to the image resolution quality. How Does GPU Scaling Work? GPU scaling works by resizing the image in real-time. It can stretch the image to fill the screen or add black bars to maintain aspect ratio, depending on the display settings. Benefits of GPU Scaling The main advantage of GPU scaling is its ability to preserve image quality while adjusting to different display resolutions.
It reduces the input lag and avoids black bars around the screen and blurry images. What is Display Scaling? Display scaling, also known as software scaling, is the process of resizing the image through the monitor or the display settings. It uses software algorithms to increase or decrease the resolution to fit the screen size.
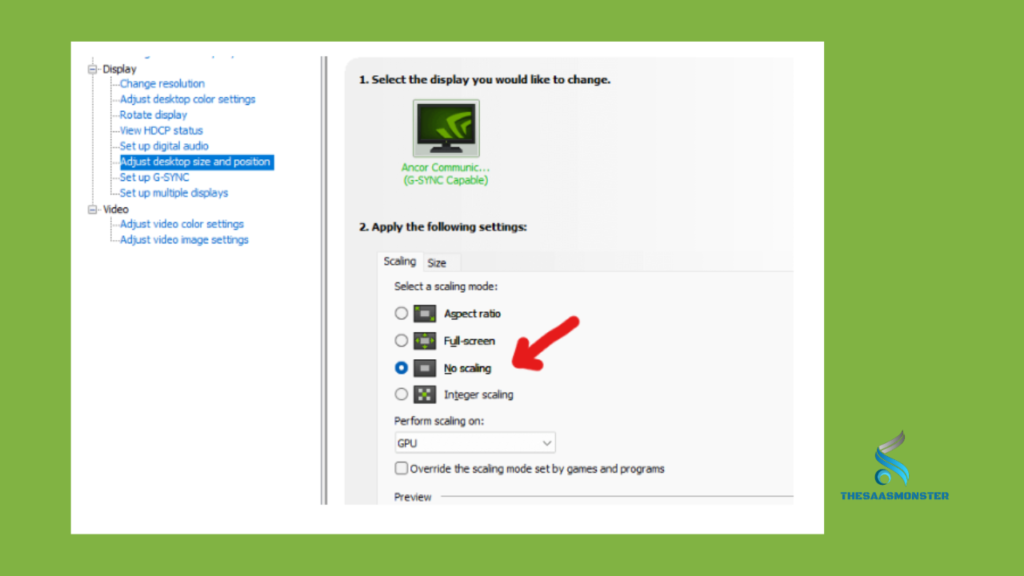
How Does Display Scaling Work? Display scaling reshapes the image to match the desired display resolution. It adds or removes pixels from the image to adjust the aspect ratio of the screen. Benefits of Display Scaling Display scaling provides clear and readable UI elements on high-resolution screens for documents, web pages, and videos. It also minimizes input lag, making it suitable for non-gaming applications.
When to Use GPU Scaling GPU scaling is optimal for gamers who prefer older games and want to maintain a smooth gaming experience on the modern screen. GPU scaling reduces the black bars around the screen and eliminates blurry images. When to Use Display Scaling Display scaling is optimal when you are more concerned with the clarity and readability of text and UI elements on high-resolution screens.
It is suitable for non-gaming applications, such as word processing, graphic design, and video editing. In conclusion, both GPU scaling and display scaling have their strengths, and the choice depends on your needs. Whichever technique you use, make sure to select the appropriate settings to avoid issues such as image distortion, input lag, and aspect ratio problems.
Read Another GPU Guides-
- What Is Shared Gpu Memory: Understanding the Significance
- Amd 8000 Series GPU: Unleashing Superior Graphics Performance
- Nvidia Geforce Rtx 4090: Unleash Ultimate Gaming Power Now!
- Gpu Backplates: Enhance Performance and Style with Custom Designs
FAQ On What Is The Difference Between Gpu Scaling And Display Scaling
Is It Better To Perform Scaling On Gpu Or Display?
For gamers who prefer older titles on modern displays, GPU scaling is recommended. However, for higher resolution screens, display scaling is the better choice for clarity and readability of UI elements. GPU scaling may cause a slightly longer input latency due to additional processing.
What Is Display Scaling?
Display scaling is a feature that adjusts the size of on-screen elements to make them readable and usable on high-resolution displays. It is often used on laptops or desktop monitors with high pixel density. Display scaling maintains the aspect ratio and sharpness of the images.
What Is Meant By Gpu Scaling?
GPU scaling refers to the process of adjusting the resolution of a video or image on a display that has a different aspect ratio than the content being displayed. This is done by the graphics processing unit (GPU) instead of the display.
It is the preferred choice for gamers who want to maintain a seamless experience on modern displays, while display scaling is better for clarity and readability of UI elements on high-resolution screens. However, GPU scaling may add a bit of input latency due to extra processing.
Does Gpu Scaling Cause Lag?
Yes, enabling GPU scaling may cause a bit of input lag due to extra processing. This may be noticeable while playing games, but it is usually insignificant in videos. Gamers who want a seamless experience on modern displays should use GPU scaling, while those who prioritize clarity and readability of UI elements should use display scaling.
Conclusion
To conclude, both GPU scaling and display scaling have their respective roles in providing optimal viewing experiences. The former is a great option for gamers who prioritize seamless performance, especially when dealing with older games, whereas the latter is better suited for users who value clarity and readability of interface elements on high-resolution screens.
Ultimately, it’s up to personal preference and specific needs to decide which option to use. Regardless, it’s essential to understand the differences between these two scaling methods to make an informed decision.