Advantages of SSD Over HDD: Unleash Lightning Speed!
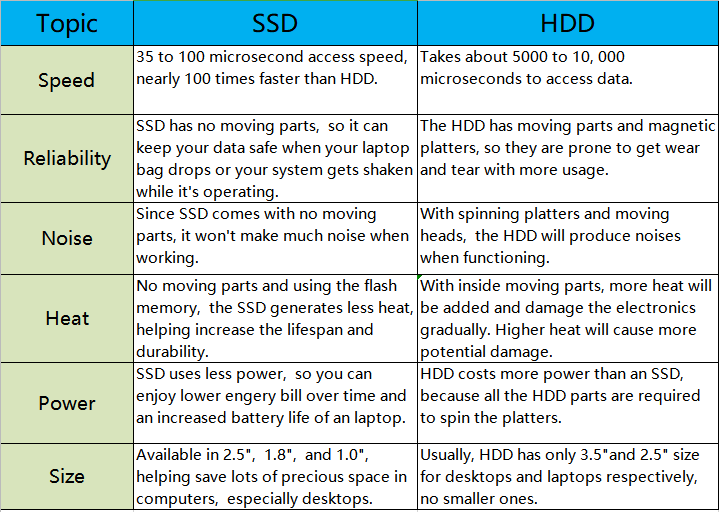
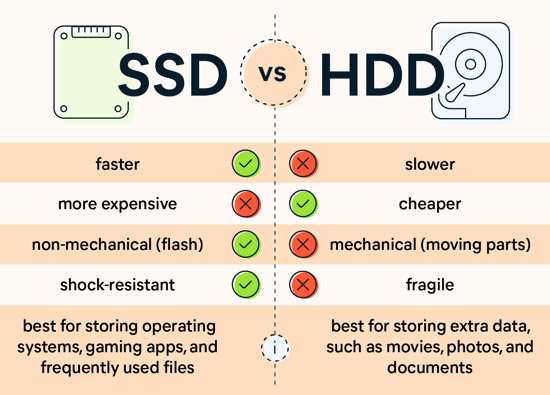
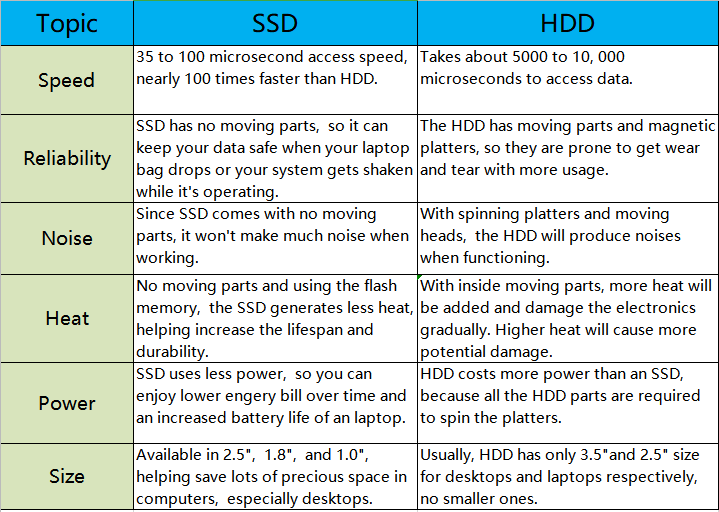
SSDs offer faster data access and improved reliability over HDDs. They consume less power and operate silently.
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have transformed the way computers handle data storage. Unlike traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), SSDs use flash memory to store data, which results in significantly faster read and write speeds. This speed boost enhances overall system performance, leading to quicker boot times and reduced application loading times.
SSDs are also more durable, as they have no moving parts, making them less susceptible to physical damage. They consume less power, which can extend battery life in laptops and reduce energy costs in data centers. With silent operation and reduced heat generation, SSDs provide a superior storage solution for both personal and professional use.
Speed And Performance
Solid State Drives (SSDs) offer significant advantages over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), especially in terms of speed and performance. This can drastically enhance user experience, making everyday tasks quicker and more efficient. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about your storage needs.
Read And Write Speeds
One of the biggest advantages of SSDs over HDDs is their read and write speeds. Unlike HDDs, which use spinning disks to read and write data, SSDs use flash memory. This allows SSDs to access data almost instantly. Here are some key points:
- SSDs: Typically offer read speeds of 550 MB/s and write speeds of 520 MB/s.
- HDDs: Generally provide read speeds of 125 MB/s and write speeds of 125 MB/s.
To better understand the difference, consider this table:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Read Speed | 550 MB/s | 125 MB/s |
| Write Speed | 520 MB/s | 125 MB/s |
These numbers clearly show that SSDs are much faster. Faster read and write speeds translate to quicker file transfers and faster program loading times. This can be particularly beneficial for tasks that involve large files, such as video editing or gaming.
Boot-up And Loading Times
Another area where SSDs outperform HDDs is in boot-up and loading times. SSDs can load your operating system and applications in a fraction of the time it takes an HDD. Here are some observations:
- Operating System Boot-up: SSDs can boot up an OS in less than 10 seconds, whereas HDDs may take up to a minute.
- Application Loading: Applications open almost instantly on SSDs, while on HDDs, it can take several seconds to minutes.
Consider this real-world scenario:
| Task | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Boot-up Time | 10 seconds | 1 minute |
| Application Loading | Instant | Several seconds to minutes |
Faster boot-up and loading times mean less waiting and more productivity. This is crucial for users who need their systems to be responsive and ready at a moment’s notice. Whether you are a professional or a casual user, the speed and efficiency of an SSD can vastly improve your computing experience.
Credit: lisisepe.gr
Read More
Durability And Reliability
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have become increasingly popular due to their numerous advantages over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). One of the most significant benefits lies in their durability and reliability. SSDs offer a level of robustness that HDDs simply cannot match. Understanding why SSDs excel in these areas can help you make an informed decision about your storage needs.
No Moving Parts
One of the primary reasons SSDs are more durable is because they have no moving parts. Traditional HDDs rely on a spinning disk and a read/write head that moves back and forth. This mechanical nature makes them susceptible to wear and tear. In contrast, SSDs use flash memory to store data. This means:
- No mechanical failures: Without moving parts, there’s less chance of mechanical breakdown.
- Less heat generation: SSDs generate less heat than HDDs, which can prolong their lifespan.
- Quieter operation: No moving parts mean that SSDs operate silently.
Let’s compare the key differences:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Moving Parts | No | Yes |
| Heat Generation | Low | High |
| Noise | None | Yes |
| Mechanical Failure | Low Risk | High Risk |
Resistance To Physical Shock
Another critical advantage of SSDs is their resistance to physical shock. Because HDDs have moving parts, they are highly vulnerable to damage from drops or bumps. SSDs, on the other hand, are more resilient. Here are some key points:
- Better shock resistance: SSDs can withstand drops and impacts better than HDDs.
- Less data loss: With no moving parts, the risk of data corruption due to physical shock is minimized.
- Longevity: Enhanced resistance to shock means SSDs often have a longer lifespan in mobile devices.
Consider the following comparison:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Shock Resistance | High | Low |
| Data Corruption Risk | Low | High |
| Lifespan in Mobile Devices | Longer | Shorter |
SSDs are ideal for laptops, tablets, and other mobile devices where drops are more likely. Their resilience to physical impacts makes them a reliable choice for anyone requiring robust data storage solutions.
Energy Efficiency
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have gained popularity over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for various reasons. One significant advantage is their energy efficiency. SSDs consume less power and generate less heat, making them ideal for a range of devices. This efficiency not only benefits the environment but also enhances the performance and lifespan of your devices.
Lower Power Consumption
SSDs use less power than HDDs, which makes them a better choice for energy savings. Traditional HDDs have moving parts like spinning disks and read/write heads, which require more power to operate. On the other hand, SSDs use flash memory with no moving parts, reducing the overall power usage.
- HDDs: Consume around 6-7 watts of power.
- SSDs: Typically use 2-3 watts of power.
To illustrate, here is a comparison table:
| Device | Average Power Consumption (Watts) |
|---|---|
| HDD | 6-7 |
| SSD | 2-3 |
SSDs also lead to longer battery life in laptops and mobile devices. Less power consumption means the battery lasts longer, which is crucial for users on the go. This makes SSDs an excellent choice for portable gadgets.
Less Heat Generation
Another advantage of SSDs is that they generate less heat. Since HDDs have moving parts, they produce more heat during operation. This heat can cause performance issues and may even damage other components in the device over time.
SSDs, with no moving parts, operate cooler. This reduced heat generation translates to better thermal management for your devices. Here are some benefits of less heat generation:
- Enhanced device performance: Less heat means components can run at optimal speeds without throttling.
- Longer device lifespan: Cooler components experience less wear and tear.
- Reduced cooling requirements: Devices with SSDs need fewer cooling mechanisms, making them quieter and lighter.
Overall, the energy efficiency of SSDs makes them a superior choice over HDDs. They offer lower power consumption and generate less heat, providing better performance and longer device lifespan.
Noise And Heat
The advantages of SSDs (Solid State Drives) over HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) are numerous. One of the most significant benefits is their performance in terms of noise and heat. SSDs are renowned for their silent operation and cooler temperatures. This makes them ideal for various applications, from personal computing to enterprise solutions.
Silent Operation
SSDs operate silently, unlike HDDs that produce noise. HDDs have moving parts, such as spinning disks and read/write heads, which generate noise. This can be distracting, especially in quiet environments.
SSDs have no moving parts. This results in a noiseless experience. This is beneficial for tasks requiring a quiet environment, such as audio recording or nighttime work.
- No spinning disks: SSDs use flash memory to store data.
- No moving parts: This eliminates mechanical noise.
- Quiet performance: Ideal for noise-sensitive applications.
Here’s a comparison table for better understanding:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Noise Level | Silent | Noticeable noise |
| Moving Parts | None | Multiple |
Cooler Temperature
SSDs generate less heat compared to HDDs. HDDs have motors and moving parts that create friction, leading to higher temperatures.
Lower heat production in SSDs helps maintain optimal performance. This is crucial for systems requiring constant high-speed data access and processing.
- Reduced friction: No moving parts means less friction.
- Lower energy consumption: SSDs consume less power, producing less heat.
- Enhanced reliability: Cooler operation extends the lifespan of the drive.
Consider this table for a quick comparison:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Low | High |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
In summary, the silent operation and cooler temperature of SSDs make them superior to HDDs in many scenarios. These features contribute to a quieter, more efficient, and reliable computing experience.
Size And Weight
Solid State Drives (SSDs) offer many advantages over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), especially in terms of size and weight. These factors are crucial for modern tech devices. Smaller and lighter components mean more portable and efficient gadgets. Let’s explore how SSDs excel in these areas.
Compact Form Factor
SSDs are known for their compact form factor. They are much smaller than traditional HDDs, fitting easily into various devices. This is especially beneficial for laptops, tablets, and even smartphones.
Here are some key points about their compact size:
- SSDs typically measure around 2.5 inches, compared to 3.5 inches for HDDs.
- They can be even smaller, such as the M.2 and NVMe SSDs, which are tiny and thin.
- The small size allows for more flexibility in device design and internal layout.
This compactness means that manufacturers can create thinner and lighter devices. For instance, ultrabooks and slim laptops often use SSDs to maintain a sleek design. The reduction in space also enables better airflow within the device, enhancing performance and cooling.
Consider the following comparison table for a clearer picture:
| Storage Type | Typical Size | Application |
|---|---|---|
| HDD | 3.5 inches | Desktops, Servers |
| SSD | 2.5 inches | Laptops, Desktops |
| M.2 SSD | 22 x 80 mm | Ultrabooks, Tablets |
Lightweight Design
Another significant advantage of SSDs over HDDs is their lightweight design. This aspect is crucial for portable devices. A lighter storage drive contributes to the overall weight reduction of the device.
Here are some benefits of their lightweight nature:
- SSDs weigh significantly less than HDDs, often less than 50 grams.
- The reduced weight makes laptops and other portable devices easier to carry.
- Lighter devices are more comfortable to use and handle, especially for long periods.
This lightweight design is particularly beneficial for travelers and mobile professionals. Carrying a laptop with an SSD is much easier on the go. The lightweight nature also contributes to better energy efficiency. Less weight means the device requires less power to operate, extending battery life.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Storage Type | Average Weight |
|---|---|
| HDD | 450 grams |
| SSD | 50 grams |
The lighter weight of SSDs is a game-changer. It transforms the user experience, making devices more portable and energy-efficient.
Credit: www.avast.com
Cost-effectiveness
Solid State Drives (SSDs) offer numerous advantages over traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). One of the most significant benefits is their cost-effectiveness. While SSDs may have a higher initial cost, their long-term savings and reduced maintenance costs make them a smart investment.
Long-term Savings
SSDs provide substantial long-term savings. Even though the upfront cost of SSDs is higher than HDDs, the overall expense over time is significantly lower. Here’s why:
- Lower Power Consumption: SSDs consume less power compared to HDDs. This translates to reduced electricity bills.
- Increased Lifespan: SSDs generally have a longer lifespan due to their lack of moving parts. This means fewer replacements and lower costs over time.
- Improved Efficiency: SSDs enhance system performance. Faster data access speeds lead to increased productivity and time savings.
Let’s compare the estimated annual costs of SSDs and HDDs:
| Cost Factor | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase Cost | $100 | $50 |
| Power Consumption (Annual) | $10 | $30 |
| Replacement Frequency (Years) | 5 | 3 |
From the table, it’s clear that the initial cost is offset by the savings in power consumption and reduced replacement frequency.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Another significant advantage of SSDs is their reduced maintenance costs. Traditional HDDs have moving parts that can wear out over time, leading to higher maintenance expenses. SSDs, on the other hand, are more reliable and require less upkeep. Here are some key points:
- No Moving Parts: SSDs have no moving parts, which reduces the risk of mechanical failure.
- Less Heat Generation: SSDs generate less heat, decreasing the need for cooling solutions and prolonging the life of other components.
- Fewer Repairs: The durability of SSDs means fewer repairs and less downtime, saving both time and money.
Consider these maintenance cost factors:
| Maintenance Factor | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling System Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Repair Costs | Minimal | Significant |
| Downtime Costs | Minimal | High |
Overall, SSDs offer lower maintenance costs, making them a more cost-effective choice over the long term.
Compatibility And Future Trends
Solid State Drives (SSDs) offer numerous advantages over traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Among these benefits, compatibility and future trends play a crucial role. SSDs not only work well with modern systems but are also poised to adapt to future technological advancements. Let’s explore these aspects in detail.
Support For Latest Interfaces
SSDs support the latest interfaces, making them highly compatible with modern devices. Key interfaces include SATA III, NVMe, and PCIe. These interfaces ensure faster data transfer rates and better performance.
- SATA III: Offers speeds up to 6 Gb/s. Common in consumer-grade SSDs.
- NVMe: Uses PCIe lanes for data transfer. Provides lower latency and higher speeds.
- PCIe: Offers multiple lanes for data transfer. Ideal for high-performance SSDs.
The table below highlights the differences between these interfaces:
| Interface | Speed | Latency | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| SATA III | Up to 6 Gb/s | Higher | Consumer-grade SSDs |
| NVMe | Up to 32 Gb/s | Lower | High-performance tasks |
| PCIe | Up to 64 Gb/s | Lowest | Enterprise solutions |
SSDs are compatible with newer motherboards and devices that support these interfaces. This compatibility ensures that users get the best performance from their systems.
Adaptability To Emerging Technologies
SSDs are adaptable to emerging technologies, making them future-proof. They integrate well with advancements in computing and data storage. Some key areas include AI, machine learning, and cloud computing.
- AI and Machine Learning: SSDs offer faster data access, crucial for AI tasks.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud services rely on SSDs for quick data retrieval.
- IoT Devices: SSDs can be embedded in IoT devices for efficient data storage.
Future trends indicate increased use of SSDs in various sectors. This includes autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and edge computing. Their adaptability ensures they remain relevant as technology evolves.
SSDs also support advanced features like encryption and wear leveling. These features enhance data security and longevity. Advanced manufacturing processes improve SSD efficiency and durability. The shift towards 3D NAND technology offers higher storage capacities and better performance.
In summary, SSDs are not only compatible with current systems but are also well-positioned to embrace future technological trends. This makes them a smart investment for any tech-savvy user.
Credit: www.diskpart.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Advantage Of Ssd Over Hdd?
SSDs offer faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs. This results in quicker boot times and file transfers. SSDs also enhance overall system responsiveness.
Are Ssds More Reliable Than Hdds?
Yes, SSDs are generally more reliable than HDDs. They have no moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. This increases their longevity.
How Do Ssds Improve Gaming Performance?
SSDs reduce game load times significantly. This allows for faster level loading and smoother gameplay. They also decrease stuttering and lag.
Do Ssds Consume Less Power Than Hdds?
Yes, SSDs consume less power compared to HDDs. This leads to longer battery life in laptops and less energy consumption overall.
Conclusion
SSDs offer faster speeds, better durability, and lower power consumption than HDDs. They enhance your device’s performance significantly. Upgrading to an SSD can improve your computing experience. For those seeking efficiency and reliability, SSDs are the superior choice. Make the switch to enjoy these benefits today.